slug
recursive
type
Post
status
Published
category
AP CSA
date
Jan 4, 2026
summary
tags
concepts
password
icon
4.17 Recursive Searching and Sorting
课时:90 minutes
一、本课回顾与目标
在之前的学习中,你已经学过:
- Linear Search(线性搜索)
- Binary Search(二分搜索)
- Selection Sort(选择排序)
- Insertion Sort(插入排序)
这些算法都是用循环(iteration)实现的。
在本课中,你将学习:
- 递归版本的 Binary Search
- 递归排序算法:Merge Sort
你将看到:
👉 递归不仅可以处理数字,也可以遍历数组、ArrayList 和字符串
二、4.17.1 Recursive Binary Search
1. 回顾:Linear Search vs Binary Search
Linear Search
- 从头到尾逐个检查元素
- 不要求数组有序
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
Binary Search
- 从中间元素开始
- 每次排除一半数据
- 必须在有序数组或 ArrayList 上使用
- 时间复杂度:O(log n)
2. Binary Search 的递归思想
递归版 Binary Search 的核心思路是:
- 检查当前范围的 中间元素
- 如果找到目标,返回索引
- 如果目标更小,只搜索左半部分
- 如果目标更大,只搜索右半部分
- 如果搜索范围为空,说明目标不存在
3. 递归 Binary Search 的 Base Case(非常重要)
递归必须有终止条件(base case)。
在 Binary Search 中,有 两个 base case:
- 中间元素等于目标值
- 搜索范围已经无效(end < start)
如果没有第二个 base case,程序会无限递归,最终导致错误。
4. 递归 Binary Search(Java 示例)
5. 思考活动
问题 1
递归 Binary Search 的 base case 是什么?
问题 2
如果要搜索数组从索引
0 到 middle,递归调用应该怎么写?问题 3
如果删除
end < start 这个判断,会发生什么?👉 程序将无法停止递归,最终出错。
三、4.17.2 Merge Sort(归并排序)
代码解读
下面我按“模块 → 关键变量 → 运行过程(带例子)→ 细节/常见坑”的顺序,把这份归并排序代码拆开讲清楚。你看完基本就能自己手写一份。
1)整体在做什么:归并排序的核心思路
归并排序 = 分而治之:
- 分(Divide):把数组不断二分,直到每一段只剩 1 个元素(1 个元素天然有序)
- 治(Conquer / Merge):把两个“已经排好序”的小段,合并成一个更大的有序段
- 最终合并回整段数组变成有序
2)类与导入
Arrays只用于Arrays.toString(data)打印数组,和排序逻辑无关。
3)入口方法:对外提供的 mergeSort(arr)
这段在做什么
- 防御式检查:
arr == null:数组根本不存在 → 直接结束arr.length <= 1:长度 0 或 1 → 已经有序 → 结束
- 真正排序从
left = 0到right = n-1
这就是“对外的干净接口”:你只要调用
mergeSort(data),不需要管下标。4)递归分解:mergeSort(arr, left, right)
4.1 递归终止条件
if (left >= right) return;
- 当
left == right时:这段只有 1 个元素,不用排了
- 当
left > right一般不会出现(正常分割不会),但写上更保险
4.2 mid 的含义
mid = (left + right) / 2
- 把区间
[left..right]分成: - 左半段:
[left..mid] - 右半段:
[mid+1..right]
4.3 这三句的逻辑顺序很关键
mergeSort(left..mid):先把左边排好
mergeSort(mid+1..right):再把右边排好
merge(left, mid, right):最后把两段“有序段”合并成一个更大的有序段
重点:merge() 的前提是两边都已经有序。所以 merge 只能放在两个递归调用之后。
5)真正的“合并”:merge(arr, left, mid, right)
目标:把
- 已排好序的左段
arr[left..mid]
- 已排好序的右段
arr[mid+1..right]
合并成一个有序段,放回
arr[left..right]5.1 临时数组 temp:为什么需要它?
- 这次合并只负责
[left..right]这一段
- 这段长度是
right - left + 1
temp用来“先装合并后的结果”,避免覆盖还没比较的原数组内容
5.2 三个指针 i、j、k 各代表什么?
i:左边“候选元素”的位置
j:右边“候选元素”的位置
k:temp 的写入位置(从 0 开始写)
5.3 主合并循环:两边都还有数的时候怎么办?
逐句解释(非常关键)
while (i <= mid && j <= right):- 左边没用完 且 右边没用完 → 才能做“左右比较”
if (arr[i] <= arr[j]):- 谁小先放谁进
temp - 这里用
<=而不是<的意义: - 稳定性:相等时优先放左边元素 → 保持原相对顺序(归并排序稳定)
- 放进 temp 后:
- 放了左边 →
i++ - 放了右边 →
j++
- 每放一个元素 →
k++
你可以把它想成“两队人排队合并”:每次挑队首更小的那个人进新队伍。
5.4 收尾:某一边用完后,另一边直接复制过去
主循环退出时只可能有两种情况:
- 左边用完了(
i > mid),右边还有
- 右边用完了(
j > right),左边还有
所以直接把剩下那一边“整段搬过去”:
这里不需要再比较,因为剩下的那部分本来就已经有序。
5.5 拷贝回原数组:把 temp 覆盖回 arr[left..right]
temp的下标从0开始
- 但它对应的是原数组的
left位置开始的一段
- 所以写回用
arr[left + p]
这一段做完之后,
arr[left..right] 就变成有序段了。6)main 测试:这段只是演示用
- 打印排序前数组
- 调用
mergeSort(data)排序
- 打印排序后数组
7)用你这组数据走一遍“分”的过程(帮助你建立直觉)
数组:
[38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10] 下标 0..6第一次分:
0..6→ mid=3 → 左0..3,右4..6
继续分:
- 左
0..3→ mid=1 →0..1和2..3 0..1→0..0和1..12..3→2..2和3..3
- 右
4..6→ mid=5 →4..5和6..6 4..5→4..4和5..5
到这里每段都是 1 个元素了,然后开始一层层 merge 回去。
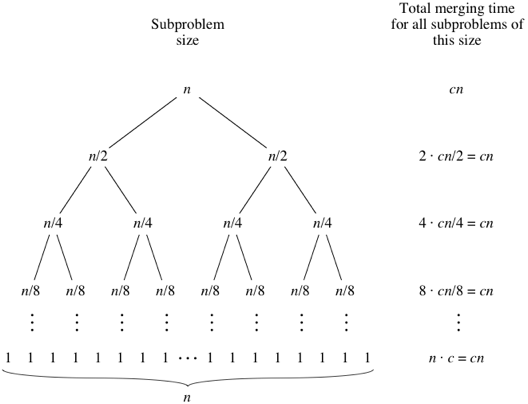
8)复杂度与特点(你背面试/考试会用到)
- 时间复杂度:O(n log n)
分成 log n 层,每层合并总量 n
- 空间复杂度:O(n)(因为需要 temp 数组)
- 稳定排序:因为用了
<=,相等元素保持原先相对顺序
1. 为什么要学 Merge Sort?
之前学过的排序算法:
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sort
它们的时间复杂度都是 O(n²)。
Merge Sort 更快,因为它像 Binary Search 一样:
- 每次把问题规模 减半
- 使用 Divide and Conquer(分治)思想
2. Merge Sort 的基本思想
Merge Sort 的过程分为三步:
- Divide
把数组拆成左右两半
- Conquer
递归排序左右两部分
- Merge
把两个有序数组合并成一个有序数组
3. Merge Sort 的关键特征(考试必认)
一个标准的 Merge Sort 通常包含:
- 3 个方法
mergeSortmergeSortHelper(递归)merge
- 使用一个辅助数组来合并数据
- 最终把结果复制回原数组
4. Merge Sort 的执行示例(Tracing)
Merge Sort 的执行示例(Tracing)
一、Merge Sort 核心思想(一句话版)
分而治之(Divide & Conquer)把数组不断 一分为二,直到只剩 1 个元素(天然有序),再 两两合并(merge),在合并过程中完成排序。
二、示例数据(用于 Tracing)
我们用一个经典的小数组,方便完整追踪:
三、递归拆分过程(Divide 阶段)

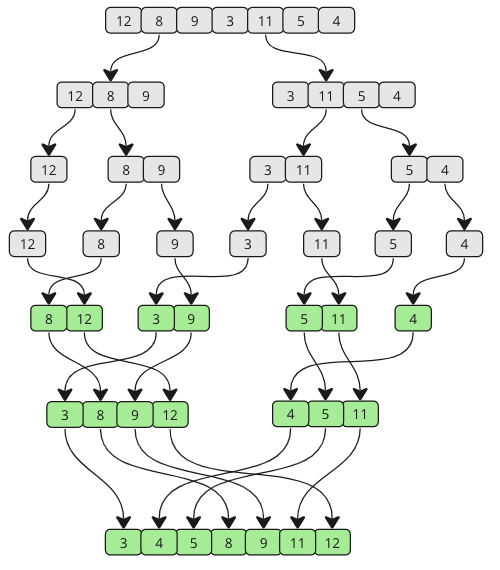
📌 关键观察(讲给学生听)
- 当子数组长度为 1 时,递归停止
- 这就是 base case
四、合并过程(Merge 阶段,重点 Tracing)
1️⃣ 合并 [3] 和 [5]
2️⃣ 合并 [8] 和 [3, 5]
3️⃣ 合并 [7] 和 [4]
4️⃣ 合并 [2] 和 [4, 7]
5️⃣ 最终合并 [3, 5, 8] 和 [2, 4, 7]
五、完整 Java 代码(标准教学版)
六、课堂强调的 4 个考点(非常重要)
✅ 1. Base Case
✅ 2. 递归做“拆分”,排序发生在 merge 中
很多学生误以为排序在 mergeSort()实际上排序发生在merge()
✅ 3. 时间复杂度(必考)
- 每一层合并:
O(n)
- 层数:
log n
- 总复杂度:
O(n log n)
✅ 4. 空间复杂度
- 需要额外数组
- 空间复杂度:
O(n)
5. Merge Sort 的时间复杂度
- 无论数据是否有序
- Merge Sort 的执行时间 始终是 O(n log n)
6. 选择题练习
问题 1
在什么情况下,Merge Sort 会执行得更快?
A. 数据已经升序
B. 数据已经降序
C. 无论如何,时间都一样
✅ 正确答案:C
问题 2
以下哪种排序算法通常最快?
A. Selection Sort
B. Insertion Sort
C. Merge Sort
✅ 正确答案:C
四、4.17.3 Tracing Challenge(追踪挑战)
挑战 1:Merge Sort 追踪
给定数组:
要求:
- 写出每一次 拆分
- 写出每一次 合并
- 直到数组完全有序
挑战 2:Recursive Binary Search 追踪
给定有序数组:
调用:
要求写出:
- 每次检查的 middle 元素
- 每次递归的
start和end
- 一共检查了多少个元素?
- 如果用 Linear Search,需要检查多少个?
五、4.17 总结(AP 考试重点)
你现在应该掌握:
- 递归可以用于遍历
- String
- 数组
- ArrayList
- Binary Search
- 必须使用有序数据
- 可以用循环或递归实现
- 通常比 Linear Search 更高效
- Merge Sort
- 是递归排序算法
- 使用 Divide and Conquer
- 时间复杂度始终是 O(n log n)
AP CSA Practice
Unit 4.17 – Recursive Searching and Sorting
Part A:Multiple-Choice Questions
(每题 1 分)
Question 1
Which of the following is a required condition for using the binary search algorithm?
A. The array must contain no duplicate values
B. The array must be sorted
C. The array must be stored in an ArrayList
D. The array must have an even number of elements
✅ Correct Answer: B
Question 2
Which statement best describes why binary search is more efficient than linear search?
A. Binary search checks fewer elements by skipping random indices
B. Binary search always finds the target in one comparison
C. Binary search eliminates half of the remaining elements each step
D. Binary search uses recursion instead of iteration
✅ Correct Answer: C
Question 3
Consider the following recursive binary search method:
Which line represents a base case?
A.
int mid = (start + end) / 2;B.
if (arr[mid] == target)C.
return binarySearch(arr, start, mid - 1, target);D.
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, end, target);✅ Correct Answer: B
(
end < start 也是 base case,但选项中只有 B)Question 4
What will happen if the condition
if (end < start) is removed from the recursive binary search?A. The algorithm will still work correctly
B. The algorithm will run faster
C. The algorithm may never stop running
D. The algorithm will always return -1
✅ Correct Answer: C
Question 5
Which of the following best describes merge sort?
A. A sorting algorithm that repeatedly swaps adjacent elements
B. A recursive algorithm that divides the array and merges sorted subarrays
C. A sorting algorithm that inserts elements into their correct position
D. A recursive algorithm that searches for a target value
✅ Correct Answer: B
Question 6
What is the time complexity of merge sort in all cases?
A. O(n)
B. O(n²)
C. O(log n)
D. O(n log n)
✅ Correct Answer: D
Question 7
Under what condition does merge sort run faster?
A. When the array is already sorted
B. When the array is sorted in reverse order
C. When the array has no duplicate values
D. It always takes approximately the same time
✅ Correct Answer: D
Question 8
Which of the following sorting algorithms must use recursion?
A. Selection sort
B. Insertion sort
C. Merge sort
D. Bubble sort
✅ Correct Answer: C
Part B:Free-Response Questions (FRQ)
FRQ 1 – Recursive Binary Search (Tracing)
(6 points)
Given the following sorted array:
A recursive binary search is called as follows:
(a)
List the value of
mid and the element checked at each recursive call until the target is found.(b)
How many elements are checked in total?
(c)
How many elements would a linear search check in the worst case for the same target?
Scoring Guidelines / Sample Answer
(a)
- Call 1: start = 0, end = 8 → mid = 4 → element = 11
- Call 2: start = 5, end = 8 → mid = 6 → element = 17
- Call 3: start = 7, end = 8 → mid = 7 → element = 20
- Call 4: start = 8, end = 8 → mid = 8 → element = 22
(b)
4 elements checked
(c)
Linear search may check 9 elements in the worst case
FRQ 2 – Recursive Method Writing
(7 points)
Write a recursive method
countOccurrences that counts how many times a given target value appears in an array.Method signature:
The method should:
- Return
0whenindexis past the end of the array
- Use recursion to count occurrences
Sample Solution
FRQ 3 – Merge Sort Conceptual Understanding
(6 points)
(a)
Explain why merge sort is considered a divide-and-conquer algorithm.
(b)
What is the base case of merge sort?
(c)
Why does merge sort always run in O(n log n) time, regardless of the initial order of the data?
Scoring Guidelines / Sample Answer
(a)
Merge sort divides the array into smaller subarrays, recursively sorts them, and then merges them back together.
(b)
The base case occurs when the subarray has one or zero elements.
(c)
The array is always divided into halves (log n levels), and merging at each level processes all n elements.
- 作者:现代数学启蒙
- 链接:https://www.math1234567.com/article/recursive
- 声明:本文采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议,转载请注明出处。
相关文章












